

Primary angioplasty, commonly known as primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI), is a minimally invasive cardiological procedure which is performed to treat narrowed or blocked coronary artery during the heart attack The procedure can be performed as a primary treatment for acute MI so as to restore the normal supply of oxygenated blood to the heart tissues.
WHAT IS ACUTE MI?
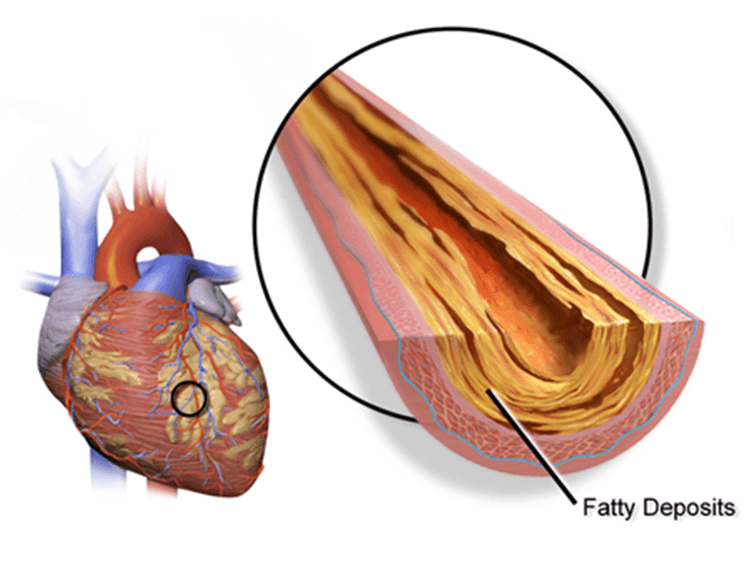
MI stands for myocardial infarction which is the medical term used for what is commonly known as a heart attack. It is a serious condition marked by the death of the myocardium which results from the lack of oxygen supply. This is usually triggered by a severe blockage in the coronary arteries which is usaully a result of clot formation over ruptured plaque. Plaque refers to the unwanted cholesterol, fats and other cellular wastes suspended in our blood that accumulate on the inner walls of the arteries and restrict the normal flow of blood. This prevents the oxygenated blood from reaching the heart muscles which leads to chronic tissue damage.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF MI?
The symptoms of the myocardial infarction are sudden and abrupt. A person experiencing the problem is likely to experience sudden onset of severe chest pain associated with difficulty in breathing. These are often accompanied by other symptoms that include:
- Pressure and tightness in the chest
- Cold sweats
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Sudden anxiety
- Rarely Unconsciousness
HOW IS THE PROBLEM DIAGNOSED?
A myocardial infarction is usually diagnosed by its symptoms and to confirm the presumption, a series of tests may be performed which include:
- Electrocardiogram (EKG)- To measure the heart's electrical activity
- Blood tests-( cardiac bio marker/ tropinin )To determine the levels of protein in your blood
- Echocardiogram- To identify the affected areas of the heart
- Angiogram- To precisely detect the blocked areas in the arteries
PRIMARY ANGIOPLASTY PROCEDURE
The procedure is performed under the influence of local anaesthesia. A small catheter fixed with a balloon on one of its end is introduced inside the patient's body via the wrist/groin . The catheter is then directed towards the blocked area with the help of special imaging technique. Once in position, the balloon is inflated to force open the walls of the narrowed artery. In case the doctors feel that the artery is not healthy enough to remain open without support, they may also place a stent to support it. After completion, the balloon is deflated and removed along with the catheter. The sheath incersion site is cleaned and covered.
POST-INTERVENTIONAL GUIDELINES
The pace at which the patient recovers greatly depends upon the extent of damage to your myocardium. The sooner you receive the treatment, the better are the chances of recovery. After the procedure, you will be shifted to an ICU and kept under observation for a day or two. Patients are usually discharged within 3 to 4 days. Some might even take a week. Certain post-intervention guidelines are to be followed for faster recovery and to alleviate the risks of reoccurrence. These include:
- The patient is required to take his medication religiously without missing any dosage. No medication should be stopped without consulting the doctors.
- If you are experiencing persistent discomfort or restlessness post the surgery, immediately inform your doctor for proper evaluation.
- Try and keep your weight under control. Try to eat healthy and stay active.
- Moderate exercises and physiotherapy should be opted for increasing the success rate of the procedures.
- Even if you feel that you are perfectly fine, it is advisable to meet your doctor for regular check-ups.
BENEFITS OF PRIMARY ANGIOPLASTY FOR ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION:
Here are a few benefits of primary angioplasty that cannot be overlooked:
- There is no unnecessary blood loss
- The convalescence period is quite short
- Angioplasty accompanied with stent placement can help to alleviate the risks of MI in future
- It helps to give instant and effective relief from the various symptoms